The decision of Polish scientific teams to engage in the development of the LOFAR system was a natural consequence of the international collaboration that the Polish radio astronomy community had been building since the 1980s, particularly through participation in the European and global Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) network. The declared intention to construct three LOFAR stations in Poland meant that Polish scientists played a significant role from the very beginning in the development and consolidation of the system.
The formal establishment of national collaboration for Poland’s participation in LOFAR took place in 2007, with the formation of the POLFAR Consortium, composed of nine institutions:
- University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn (coordinator),
- Jagiellonian University in Kraków,
- Space Research Centre of the Polish Academy of Sciences in Warsaw,
- Poznań Supercomputing and Networking Center (affiliated with the Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry of the Polish Academy of Sciences),
- University of Zielona Góra,
- Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń,
- Nicolaus Copernicus Astronomical Center of the Polish Academy of Sciences in Warsaw,
- Wrocław University of Environmental and Life Sciences,
- University of Szczecin.
From 2007 to 2020, the first chair of the consortium was Prof. Katarzyna Otmianowska-Mazur (Jagiellonian University). The position is currently held by Prof. Andrzej Krankowski (University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn).
In 2010, the consortium successfully applied to include LOFAR in the first Polish Roadmap for Research Infrastructures — a key tool of national science policy used for long-term planning and strategic research infrastructure development, enabling Polish research teams to participate in major European and international initiatives.
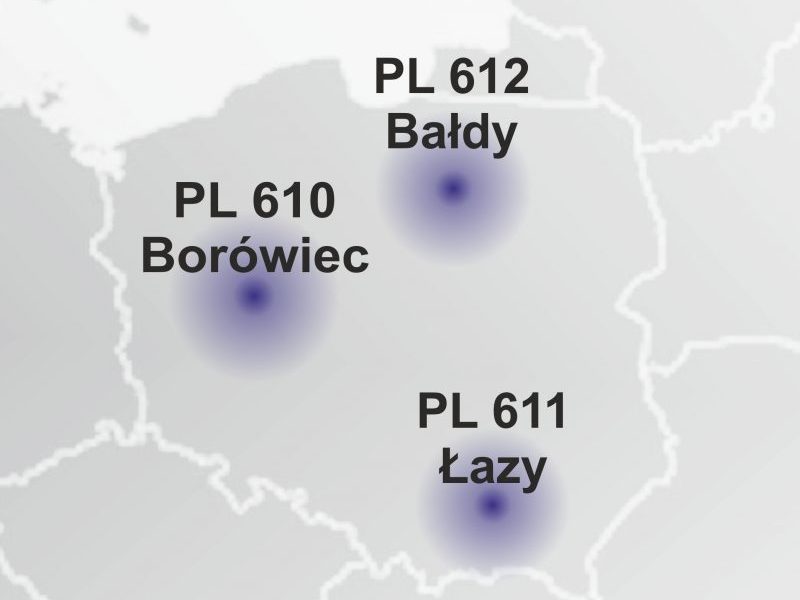
This inclusion was crucial for obtaining funding in 2013 from the Ministry of Science and Higher Education for the construction of three Polish LOFAR stations, under the framework for financing large research infrastructure. The funding enabled the consortium to commission the construction of the stations in Bałdy (near Olsztyn), Borówiec (near Poznań), and Łazy (near Kraków). These stations are managed respectively by the University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn, the Space Research Centre PAS in Warsaw, and the Jagiellonian University in Kraków. The funds also allowed for the connection of the Polish stations to the LOFAR data network through the PIONIER national fiber-optic infrastructure.
At the beginning of 2016, the Polish stations became a functional part of the LOFAR system and began conducting radio astronomical observations and space environment monitoring within the Key Science Projects of LOFAR as part of the International LOFAR Telescope (ILT).
Since 20 December 2023, by Implementing Decision (EU) 2023/2881 of the European Commission, the Polish LOFAR stations, along with the POLFAR consortium, have become part of the Low Frequency Array European Research Infrastructure Consortium) (LOFAR ERIC).